|
Home |
Consulting |
Training |
Expert Witness |
Failure Analysis |
Design Review |
Corrosion Test |
Corrosion Software
|
Coatings
|
Materials Selection |
Cathodic Protection |
>>> |
|
 Corrosion Modeling Software and Corrosion Prediction Software Series DWD-Compass®: Modeling and Prediction of Corrosion in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Highly Effective Software Solutions to Copper Tube Corrosion in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Version 9.20
Anytime Anywhere Any Device Any OS
No USB dongles No
installation
No Browser Plug-ins
|
|
Why WebCorr |
Performance Guarantee |
Unparalleled Functionality |
Unmatched Usability |
Any Device Any OS |
Free Training
& Support |
CorrCompass |
|
|
|
|
|
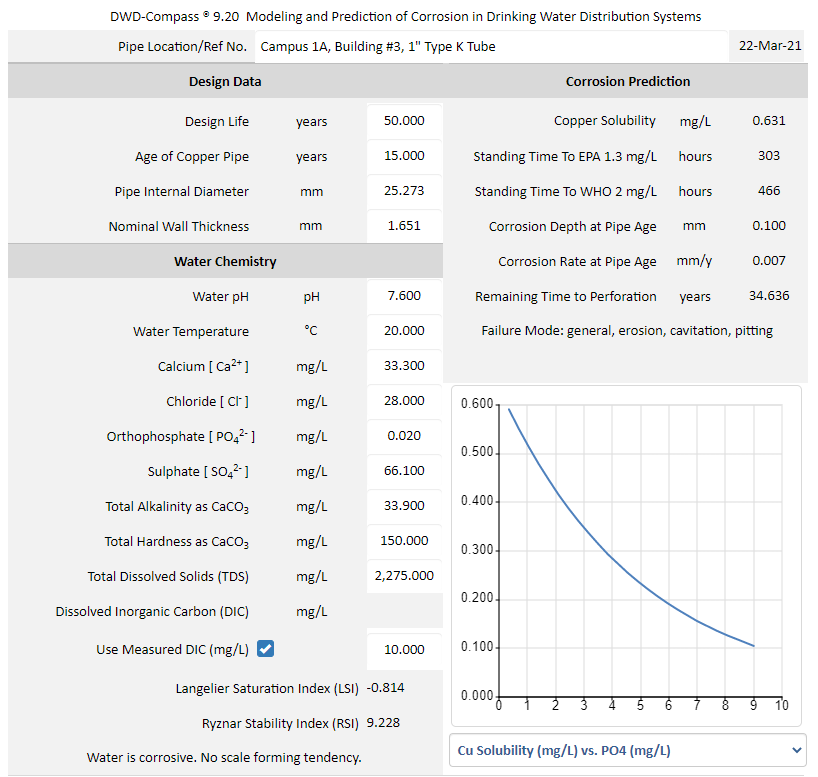
Under the water chemistry shown in Figure 1 below, DWD-Compass predicts that the copper solubility is 0.565 mg/L, the standing time to reach the US EPA's action level of 1.3 mg/L is 303 hours, the standing time to reach the WHO's limit of 2.0 mg/L is 466 hours, the corrosion rate of copper tube is 0.007 mm/y, the corrosion depth is 0.1 mm, the time-to-perforation is 34.363 years, and the mode of failure is general corrosion, erosion, cavitation, and pitting. DWD-Compass also predicts the scaling tendency of the specified water chemistry. The commonly used Langelier Saturation Index (LSI) and Ryznar Stability Index (RSI) are computed for the prevailing operating conditions. The corrosivity of water is predicted and classified in accordance with the LSI results. In Figure 1 below, DWD-Compass predicts that the specified water chemistry is corrosive and has no scale forming tendency. 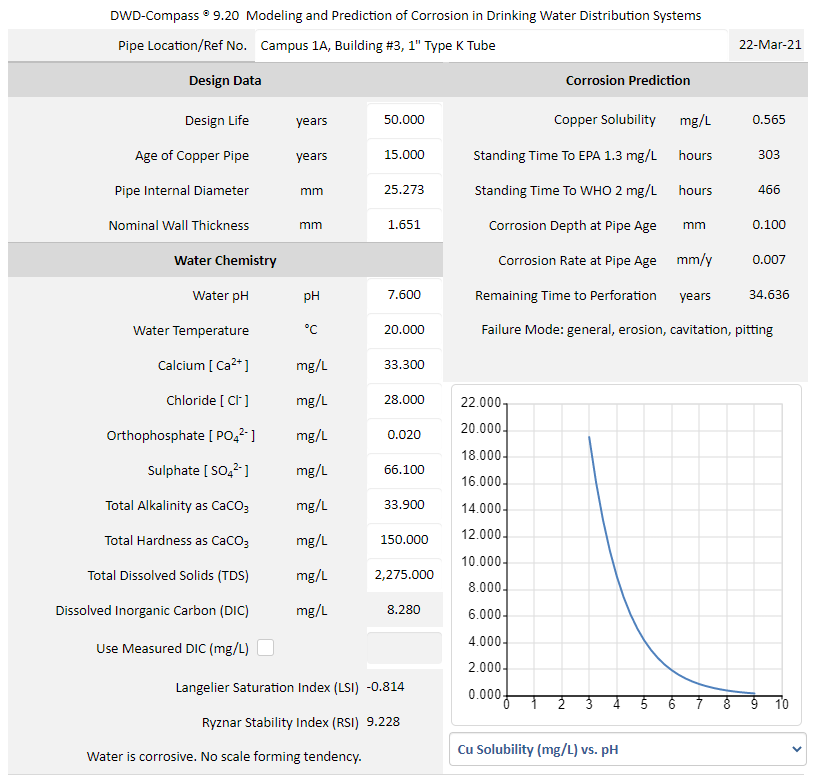 Figure 1 Overview of DWD-Compass.
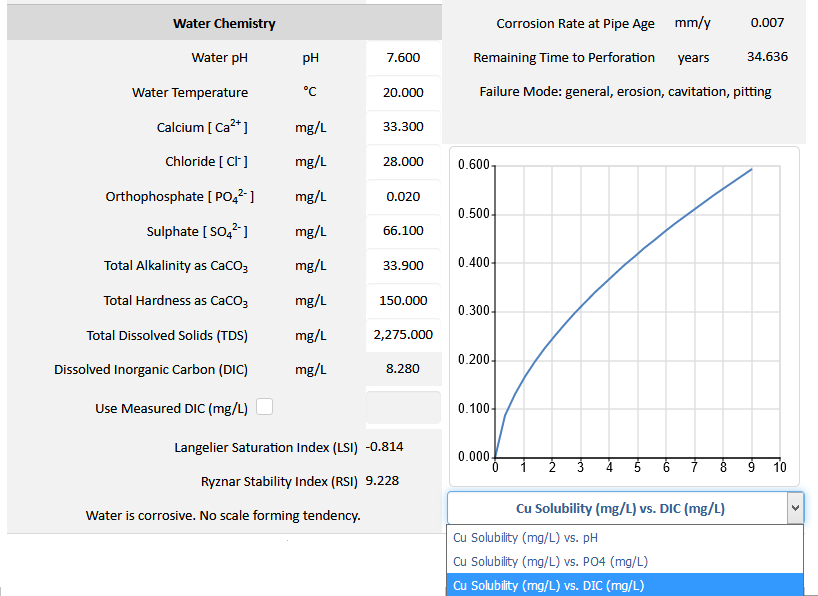
DWD-Compass models the effects of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and orthophosphate on copper tube corrosion in drinking water distribution systems. The predictive engine in DWD-Compass determines the DIC based on the specified water chemistry (Figure 1). If DIC is included in the water analysis report, users of the DWD-Compass has the option to override the predicted value by checking the "Use Measured DIC (mg/L)" box (Figure 2) and enter the measured DIC for use by the software. The effects of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and orthophosphate on cuprosolvency are plotted in Figure 2 and Figure 3 respectively.
Figure 2 DWD-Compass models the effect of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) the copper solubility.
Figure 3 DWD-Compass models the effect orthophosphate on the copper solubility. Using DWD-Compass is as easy as 1-2-3: (1) Enter the copper tube design data; (2) Enter the water chemistry; (3) Review the prediction results (Plotting options include: Cu solubility vs. pH; Cu solubility vs. PO4; Cu solubility vs. DIC).
The powerful applications of DWD-Compass are truly unlimited in modeling and predicting corrosion in drinking water distribution systems. Contact us for licensing details. |
|
|
DWD-Compass, giving you the right directions in managing corrosion in drinking water distribution systems. |
|
|
Home | Contact Us | PDF |
Copyright © 1995-2026. WebCorr Corrosion Consulting Services. All rights reserved. |

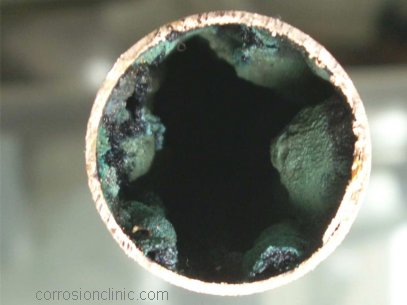 Pinhole
leaks in copper pipes and tubing in potable water distribution systems
in hotels, hospitals, homes and other residential, commercial, and
industrial buildings have been on the rise in recent years. The
insidious leaks not only cause losses of water but may also cause
serious damages to the walls, ceilings, fittings, furniture, equipment
and other neighboring structures. The leaks often raise health concerns
of the quality of drinking water.
Pinhole
leaks in copper pipes and tubing in potable water distribution systems
in hotels, hospitals, homes and other residential, commercial, and
industrial buildings have been on the rise in recent years. The
insidious leaks not only cause losses of water but may also cause
serious damages to the walls, ceilings, fittings, furniture, equipment
and other neighboring structures. The leaks often raise health concerns
of the quality of drinking water.