|
Home | Consulting | Training | Expert Witness | Failure Analysis | Design Review | Corrosion Test | Corrosion Software | Protective Coatings | Materials Selection | Cathodic Protection | >>> | ||
|
Course Outline |Who Should Attend |Registration |In-House |On-Demand |Online Courses |PPT Slides+Testbank |Course List | Why WebCorr |
||
| Course Overview | ||
|
This electroplating course can be taken as in-house training course, course-on-demand, online course and distance learning course worldwide. It can also be customized to meet the specific needs of your organization.
|
||
|
||
| Course Outline | ||
|
|
||
|
1.1 Overview of Electroplating Technology 1.2 Electroplating: Basic Terms and Concepts
1.2.2 Redox Reactions 1.2.3 The Electromotive Force (EMF) Series
1.2.4 Equilibrium Potential, Overpotential
1.2.5 Effect of Concentration on
Potential 1.2.6 Anode, Cathode and Cell Potentials 1.2.7 Conductivity of Electrolyte 1.2.8 Electrolysis and Faradayís Law 1.3 Electroplating: Electrode Kinetics 1.3.1 Kinetics of Electrodeposition (Tafel & Butler-Volmer Equation) 1.3.2 Polarisation and Mass Transport (Diffusion) 1.3.3 The Double Layer 1.3.4 Rate-Determining Steps in Electrode Reactions Concentration Overvoltage Charge-Transfer Overpotential Crystallisation Overvoltage Resistance Overvoltage 1.4 Materials That Can Be Electroplated: Understanding the Atomic Structure of Metals and Alloys 1.4.1 The Crystalline Nature of Metals 1.4.2 Lattice Defects in Metals 1.4.3 Grains and Grain Boundaries 1.4.4 Lattice Defects in Alloys 1.4.5 Effect of Lattice Defects on the Mechanical Property 1.4.6 Metals That Can Be Electrodeposited 1.5 Electroplating Processes and Process Control 1.5.1 Overview of Electrodeposition 1.5.2 Essential Components of a Plating System 1.5.3 The Nature of Plating Process 1.5.4 Electroplating Electrolytes 1.5.5 Mass and Current Relationship 1.5.6 Current Efficiency 1.6 Exercises and Case Studies
2.1 Electrodeposition Considered at the Atomistic Level 2.1.1 Mechanisms of Electrodeposition 2.1.2 Electrocrystallisation: Nucleation and Growth of Nuclei 2.1.3 Kink Site and Surface Imperfections 2.1.4 Overall Phase Growth 2.1.5 Effects of Plating Additives on the Structure and Properties of Electrodeposits 2.1.6 Other Factors Influencing the Quality of Electrodeposits 2.1.7 Thickness and Porosity 2.1.8 Whisker Growth 2.2 Different Plating Processes 2.2.1 Direct Current Electroplating 2.2.2 Pulse Current Electroplating Process 2.2.3 Periodic Pulse Reverse Plating Process 2.2.4 Effects of Pulse Current, Pulse Shape and Time on the Electrodeposits 2.2.5 Laser-induced Plating 2.2.6 Comparison of Different Plating Processes 2.3 Electroless Plating and Immersion Plating 2.3.1 Fundamentals of Electroless Deposition 2.3.2 Composition of Electroless Plating Bath 2.3.3 Operating Conditions of Electroless Plating Baths 2.3.4 Properties of Electroless Deposits 2.3.5 Applications of Electroless Deposition 2.3.6 Electroless Deposition of Composites 2.4 Exercises and Case Studies 2.5 Electrophoretic Deposition 2.5.1 Introduction to Electrophoretic Deposition 2.5.2 Mechanisms of Electrophoretic Deposition 2.5.3 Kinetics of Electrophoretic Deposition 2.5.4 Applications of Electrophoretic Deposition
3.1 Surface Preparation of Substrate
3.1.1
Importance of Surface Preparation 3.2 Selection of Plating Materials 3.2.1 Decorative Properties 3.2.2 Solderability and Weldability 3.2.3 Antifriction Properties 3.2.4 Corrosion Resistant Properties 3.2.5 Electrical Contacts and Conductivity 3.2.6 Hardness and Wear Resistant Properties 3.2.7 Other Properties 3.2.8 Thickness of Electrodeposits 3.3 Selection of Plating Bath 3.4 Electroplating of Copper and Copper Alloys 3.5 Electroplating of Silver and Its Alloys 3.6 Electroplating of Gold and Its Alloys 3.7 Electroplating of Nickel and Its Alloys 3.8 Electroplating of Tin, Lead, Cadmium and Their Alloys 3.9 Electroplating of Zinc and Its Alloys 3.10 Electroplating of Chromium 3.11 Electroplating of Iron and Its Alloys 3.12 Electroplating of Palladium and Platinum 3.13 Exercises and Case Studies
4.1 Electroless Deposition of Copper 4.2 Electroless Deposition of Nickel 4.3 Electroless Deposition of Silver 4.4 Electroless Deposition of Gold 4.5 Electroless Deposition of Palladium and Platinum 4.6 Electroless Deposition of Alloys 4.7 Properties of Electrodeposited Metals and Alloys 4.7.1 Electrical and Electronic Properties 4.7.2 Mechanical Properties 4.7.3 Porosity and Thickness of Deposit 4.7.4 Corrosion Resistance Properties 4.7.5 Solderability and Weldability 4.8 Electroplating Process Control and Chemical Analysis of Plating Solutions 4.8.1 Plating Solution Make-up and Analysis Techniques 4.8.2 Current Density, pH, Temperature and Conductivity 4.8.3 Cathode Efficiency and Anode Efficiency 4.8.4 The Hull Cell Test 4.8.5 Covering Power and Throwing Power 4.8.6 Process Monitoring 4.9 Methods for Testing and Evaluation of Electrodeposits4.9.1 In-situ Observation of Electrodeposition by SPM/STM/SFM 4.9.2 DC Potential Measurement 4.9.3 DC Polarization Measurement 4.9.4 AC Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) 4.9.5 Mass Spectrometric Methods: ISS/SIMS/SNMS 4.9.6 Electron Spectroscopic Methods: XPS/ESCA/AES 4.9.7 Microscopy and Microanalysis: SEM/TEM/EDX/WDX 4.10 Exercises and Case Studies
5.1 Troubleshooting of Electroplating Operations and Electrodeposits 5.1.1 The 10-Points General Guide for Troubleshooting Electroplating Operations
5.1.2 Troubleshooting Guide for Acid Copper Sulfate Plating 5.2 Electroforming: Processes and Applications 5.3 Anodizing: Processes and Applications 5.4 Chromating: Processes and Applications 5.5 Phosphating: Processes and Applications 5.6 Electroplating Waste and Waste Treatment 5.7 Exercises and Case Studies 5.8 End-of-Course Examination
|
||
|
Course Outline |Who Should Attend |Registration |In-House |On-Demand |Online Courses |PPT Slides+Testbank |Course List |
||
| Who Should Attend This Electroplating Course | ||
|
Plating technicians, plating operators, technical/sales representatives, process engineers and project managers, and QA/QC personnel working in the electroplating and metal finishing industry.
|
||
| Registration for This Electroplating Course | ||
|
Click here to register for this short course online, or Click here to download this short course brochure with registration form in PDF format.
|
||
| In-House Training Courses and On-Site Training Courses | ||
|
If you are concerned with corrosion in your business, in-house training is a great solution to train a group of employees from design, production, operation, quality assurance, inspection and maintenance, and technical sales and support on corrosion control and corrosion prevention technology. The contents of all corrosion courses can be customized to fit your organization's needs.
There is no minimum or maximum number of participants required for in-house training corrosion courses. We conduct the in-house training corrosion course at your company's premises and at a time convenient to your company. Requests for in-house training corrosion courses from overseas countries are also welcome.
Click here to contact us for a quotation.
|
||
| Corrosion Course-On-Demand | ||
|
All our publicly scheduled corrosion short courses are conducted once a year. However, you do not need to wait for one year if you have missed any of the publicly scheduled corrosion courses as we have this unique corrosion course-on-demand scheme: we will conduct the course just for you on an one-on-one basis at a time and in a location convenient to you. This option costs significantly less than a full-scale in-house training program.
Click here to contact us for a quotation for taking this course as course-on-demand.
|
||
| Online and Distance Learning Corrosion Courses | ||
|
Click here to register this corrosion short course for online or distance learning. |
||
| PowerPoint Slides and Test Bank (with Solutions) for Trainers, Instructors, Tutors, University Lecturers and Professors | ||
|
If you are involved in teaching or training, you may wish to purchase a complete set of the trainer's package for this training course. The trainer's package comes complete with ready-to-use PowerPoint slides (fully editable) and test bank (with answer keys). These ready-to-use PowerPoint slides contain high quality color photographs, illustrations, animations, audio and video clips. The test bank contains questions in four categories: (1) true or false, (2) multiple choice, (3) calculation, and (4) reasoning and open-ended discussions. The trainer's package is suitable for in-house training and university teaching (30 lecture hours). This is exactly the same package that WebCorr uses to deliver our current training course. The one-time lump sum fee allows your organization to use the training package and also modify it. For example, your organization may modify the course contents and re-name/re-brand the course under your organizationís name. WebCorr only retains the copyright of the original PowerPoint slides and test bank.
Click here to contact us if you need more information on the trainer's package. |
||
|
Course Outline |Who Should Attend |Registration |In-House |On-Demand |Online Courses |PPT Slides+Testbank |Course List |
||
|
Copyright © 1995-2025.. All rights reserved. |
||
 This 5-day electrodeposition course thoroughly and
systematically covers the fundamentals, processes, and applications of electroplating,
electroless plating, immersion plating, electroforming, anodizing, and
electrophoretic deposition (of ceramics and paints).
Participants will learn the fundamentals of electrodeposition processes,
the effects of process variables on the plating quality, and the various plating
techniques such as DC electroplating, pulse electroplating, electroless
plating and immersion plating. Modern techniques for the testing and evaluation
of electrodeposits and practical methods for trouble-shooting
electroplating and electroless plating baths are also presented in this short course.
This 5-day electrodeposition course thoroughly and
systematically covers the fundamentals, processes, and applications of electroplating,
electroless plating, immersion plating, electroforming, anodizing, and
electrophoretic deposition (of ceramics and paints).
Participants will learn the fundamentals of electrodeposition processes,
the effects of process variables on the plating quality, and the various plating
techniques such as DC electroplating, pulse electroplating, electroless
plating and immersion plating. Modern techniques for the testing and evaluation
of electrodeposits and practical methods for trouble-shooting
electroplating and electroless plating baths are also presented in this short course.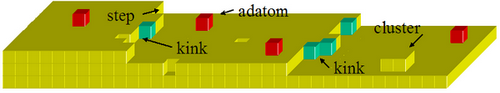
 1.2.1 Primer on Chemistry
1.2.1 Primer on Chemistry